Synthetic rubber is very important in making things today. In 2023, it made up almost 58% of all rubber used in the world. The most common types of synthetic rubber are:
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Polybutadiene Rubber (BR)
Ethylene-Propylene-Diene Monomer (EPDM)
Isobutylene-Isoprene Rubber (IIR)
Polyisoprene Rubber (IR)
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
Acrylic Rubber (ACM)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Synthetic rubbers are also called elastomers. They are made by people, not found in nature. These elastomers are often stronger and last longer than natural rubber. They are used in many industries, like car making and building. Knowing about the different kinds of rubber helps engineers and workers pick the right one for each job. The table below shows how much synthetic rubber was sold around the world in recent years:
| Year | Global Synthetic Rubber Market Size (USD Billion) |
| 2023 | ~41.04 |
| 2024 | 38.90 |
| 2025 | 41.04 (projected) |
| 2034 | 66.44 (forecast) |
Key Takeaways
Synthetic rubber is made by people. It is used a lot in tires, seals, hoses, and many other things. It lasts longer than natural rubber. It can also be changed to fit different jobs.
There are different types of synthetic rubber. Each type has its own special strength. SBR is good for tires. NBR works well with oil. EPDM is best for bad weather. Silicone is used for heat and in medicine.
You need to pick the right synthetic rubber for each job. Think about things like temperature, chemicals, how bendy it is, and how much it costs.
Many synthetic rubbers, like Santoprene, can be used again. This helps cut down on trash and keeps the earth cleaner.
Knowing what each rubber can do helps engineers and makers. They can choose the best one. This makes products stronger, safer, and last longer.
What Is Synthetic Rubber?
Definition
Synthetic rubber is made by people, not found in nature. It acts a lot like natural rubber. These materials are called elastomers because they can stretch and go back to their shape. Factories make elastomers using chemicals from oil. Synthetic rubber is a lot like natural rubber, but it can be changed for special jobs.
Note: There are many kinds of synthetic rubber, like styrene-butadiene rubber, butyl rubber, and silicone rubber. Each kind is strong in its own way and used for different things.
The chemical industry says synthetic rubber is any elastomer that can be vulcanized and is made by joining chemicals together. This group has acrylate rubbers, butadiene-styrene copolymers, nitrile-butadiene rubbers, and others. These elastomers are important for making tires, seals, hoses, and many other things.
Production
Making synthetic rubber starts with oil-based materials. Factories use things like naphtha, which reacts with natural gas to make monomers. Monomers are things like butadiene, styrene, isoprene, chloroprene, acrylonitrile, ethylene, and propylene. Polymerization is the process that links monomers to make long chains called polymers.
Most elastomers have a backbone made of carbon atoms, but silicone rubber has a backbone made of silicon and oxygen.
Silicone rubber comes from silicon, which is found in sand or quartz.
Different catalysts and monomer mixes help control how the elastomers turn out. After polymerization, the material goes through vulcanization. This step uses things like sulfur to make the rubber harder and stronger. Changing the chemical structure lets factories make elastomers for many special uses.
Types of Synthetic Rubber
Styrene-Butadiene (SBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber is used a lot around the world. Factories make it by mixing mostly butadiene and some styrene. This mix creates a material that is both strong and bendy. SBR does not wear down easily and sticks well to metal. It works in very cold and hot places, from -60ºF to +225ºF. SBR is mostly used to make tires, which use most of the SBR made. It is also found in belts, hoses, wires, shoe soles, and food packaging. SBR is not expensive and works well for many jobs. People often mix SBR with natural rubber to make tires better.
Note: SBR is mixed with natural rubber to help tires last longer.
Butadiene Rubber (BR)
Butadiene rubber is another important kind of synthetic rubber. It is very bouncy and can stretch a lot. BR does not tear easily and lasts a long time. It works well in both hot and cold weather. BR is used in tires, gaskets, seals, and shoe soles. It is also found in conveyor belts, sports gear, and medical items.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber is also called Buna-N. It is made from acrylonitrile and butadiene. NBR is very good at resisting oil, fuel, and chemicals. It is used for seals, gaskets, and hoses in cars and planes. NBR is also used in oil and gas tools and medical gloves. It works well in engines and fuel systems because it does not break down in oil. NBR is strong and lasts a long time in tough places.
Ethylene Propylene Diene (EPDM)
EPDM is a synthetic rubber that stands up to sun, rain, and ozone. It stays bendy in both hot and cold weather. EPDM does not get damaged by water or many chemicals. It is cheap and can be recycled. EPDM is used in car doors, hoses, roofs, and air systems. It is a good choice for things used outside or in rough weather.
Neoprene (CR)
Neoprene is also called chloroprene rubber. It is tough, bendy, and does not get ruined by oil. Neoprene can handle stress and changes in temperature. It is used in cars for gaskets, hoses, and mounts. In buildings, it is used for seals and pads. Neoprene is also found in wetsuits, safety gear, and belts because it resists weather and chemicals.
Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl rubber does not let gas pass through easily. This makes it great for tire tubes and medicine bottle caps. It stays bendy and keeps air inside tires. Butyl rubber also protects medicine from water and chemicals. It can be changed to fit special needs, like making it cure faster for medicine seals.
Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE)
Chlorinated polyethylene is a strong and flexible synthetic rubber. It stands up to heat, oil, fire, and bad weather. CPE is used for wire covers, hoses, and car parts. It is easy to mix and shape. CPE works well in many temperatures and does not catch fire easily.
Acrylic Rubber (ACM)
Acrylic rubber is used a lot in cars. It can take high heat, oil, and does not get old fast. ACM is found in seals, hoses, gaskets, and glue. It helps cut down noise and makes car parts last longer. ACM is also good for fuel system parts and glue for car doors.
Fluorocarbon (FPM)
Fluorocarbon rubber is also called FPM or Viton. It has fluorine in its structure. FPM can handle very high heat and strong chemicals. It does not break down in oil, fuel, or solvents. FPM is used for seals and gaskets in cars, planes, and factories. It works well where things get very hot or have harsh chemicals.
Silicone Rubber (MQ)
Silicone rubber is very bendy and can take high heat. It is safe for people and does not react with chemicals. In electronics, it covers wires and seals parts. In hospitals, it is used for tubes, catheters, and implants. Silicone rubber is clear and soft, so it is good for medical and dental tools.
Polyisoprene
Polyisoprene is a synthetic rubber that is a lot like natural rubber. It does not have latex proteins, so it does not cause allergies. Polyisoprene is used for medical and food items. It is easy to make and does not break down in ozone or chemicals. Polyisoprene is not as stretchy as natural rubber, but it is more even and safe for people with allergies.
Santoprene
Santoprene is a special rubber that acts like both rubber and plastic. It is made by mixing EPDM rubber with polypropylene. Santoprene can be used again and again, which is good for the planet. It stands up to chemicals, weather, and bending. Santoprene is used in car seals, hoses, and home products. It is also found in appliances and outdoor items. New types of Santoprene are easier to make and cost less.
| Feature/Property | Description | Automotive Uses | Consumer Goods Uses |
| Material Type | Santoprene is made from EPDM rubber and polypropylene | Used for car seals, hoses, and inside and outside car parts | Used in home appliances, wires, and outdoor products |
| Durability | Very tough and does not wear out easily | Makes car parts last longer and resist damage | Makes home items strong and able to handle stress |
| Chemical Resistance | Does not get ruined by acids, oils, or grease | Good for car parts that touch fluids | Good for home items that touch chemicals |
| Weather Resistance | Does not crack in sun or rain | Used for car parts outside | Used for outdoor home products |
| Temperature Range | Works from very cold to very hot | Used in car air systems and hoses | Good for appliances that get hot or cold |
| Recyclability | Can be recycled and used again | Helps car makers be more green | Good for the environment |
| Processability and Surface Quality | New Santoprene is easy to shape and looks nice | Used for car parts that need to look and feel good | Makes home items flexible and nice looking |
| Aesthetic and Functional Qualities | Strong, bendy, and looks good | Used for car interiors and panels | Used for home items that need to be tough and look good |
Santoprene is a top choice for cars and home goods because it is strong and flexible.
Buna Rubbers
Buna rubbers include Buna-N and Buna-S. Buna-N is made from acrylonitrile and butadiene. It is very good at resisting oil and fuel. Buna-S is made from styrene and butadiene. It stands up to heat and chemicals. Buna-N is used for seals and hoses. Buna-S is used in tires, belts, and shoe soles. Factories can change how these rubbers are made to fit different needs.
EPM
Ethylene propylene rubber, or EPM, is a synthetic rubber with a strong backbone. It does not get damaged by heat, sun, or weather. EPM stays bendy in the cold and is good at stopping electricity. It is used in car doors, hoses, roofs, and cables. EPM is tough and flexible, so it works well in cars and buildings.
Epichlorohydrin (CO)
Epichlorohydrin rubber is very good at resisting oil, fuel, and chemicals. It keeps its strength in tough places and does not let gas pass through. CO rubber is used for fuel hoses, seals, and gaskets in cars and planes. It works in both cold and hot weather and bends well. CO rubber sticks well to metal and fabric, which helps make strong seals.
Tip: When picking a type of rubber, think about what you need. Check if it can handle the right temperature, chemicals, and how much it can bend.
Properties and Uses
Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance means how well rubber stands up to rubbing. Nitrile rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber are very good at this. Nitrile rubber is used in car hoses, fuel lines, O-rings, and seals. It does not wear out fast and can handle oil. Styrene-butadiene rubber is picked for tires, shoe soles, belts, and floors. Polyurethane is also strong against wear in factories. Neoprene and Viton do a good job but not as well as Nitrile or SBR. EPDM and silicone do not resist wear as much and are not best for rough jobs.
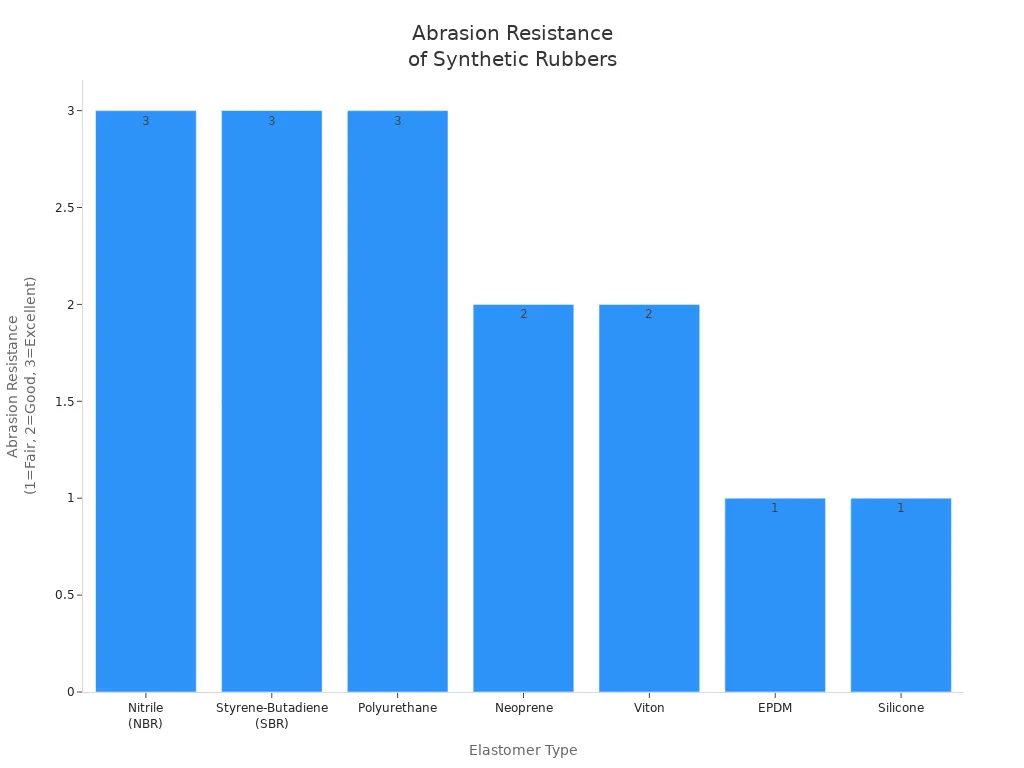
| Elastomer | Abrasion Resistance | Typical Critical Applications |
| Nitrile (NBR) | Excellent | Automotive hoses, fuel lines, O-rings, gaskets, seals |
| Styrene-Butadiene (SBR) | Excellent | Automotive tires, shoe soles, conveyor belts, industrial flooring |
| Polyurethane | Excellent | Industrial applications requiring high wear resistance |
| Neoprene | Good | General purpose, less than NBR, SBR, Polyurethane |
| Viton | Good | Aerospace seals, chemical and fuel handling |
| EPDM | Fair | Less suitable for abrasion-critical uses |
| Silicone | Fair | High temperature, poor abrasion resistance |
Oil and Chemical Resistance
Some synthetic rubbers can handle oil and chemicals very well. Nitrile butadiene rubber is great with oils, fuels, and grease. Viton is even better with strong chemicals and oil. This makes it good for planes and chemical plants. Neoprene is strong and can handle oil and chemicals too. It is used in gloves, wetsuits, and seals. These rubbers stop leaks and keep machines safe in cars, planes, and food factories.
NBR stands up to oil, fuel, acids, bases, and cleaners.
Viton works with harsh chemicals and high heat.
Neoprene is picked for many jobs because it is strong and resists oil.
Weather and Heat Resistance
Rubbers that resist weather and heat are needed outside and in hot places. EPDM rubber does not get ruined by sun, ozone, or rain. It is used for car seals, roofs, and hoses outside. Silicone rubber stays soft and keeps its shape in very high heat, up to 572°F. Viton is good in tough places, handling both heat and chemicals. These rubbers are used in cars, factories, and buildings where weather and heat can cause problems.
EPDM is best for outdoor seals and roofs.
Silicone is used in oven gaskets, medical tools, and electronics.
Viton is chosen for planes and chemical plants.
Gas Impermeability
Some rubbers are better at blocking gas than others. Butyl rubber keeps air from passing through, so it is used in tire tubes and liners. Epichlorohydrin rubber also blocks gas well and is used in fuel systems. EPDM is good for stopping gas, especially in steam and brake parts.
| Synthetic Rubber | Gas Impermeability Characteristics | Main Uses |
| Butyl Rubber | High impermeability to gases; low thermal expansion | Tire inner tubes, tire liners, sidewalls |
| Epichlorohydrin (ECO) | Superior gas impermeability compared to Nitrile | Fuel systems |
| EPDM | Good for high-temp water vapor | Seals for steam, brake system parts |
Specialty Applications
Some rubbers are picked for special jobs. Neoprene is used for tubing, wire covers, and safety clothes. Nitrile rubber is used in oil hoses, fuel tanks, and even rocket parts. Hydrogenated NBR keeps air out very well. Butyl rubbers are good at blocking gas and stopping electricity. EPDM is used in car parts and shoes because it stands up to weather. Urethane elastomers, like spandex, are found in stretchy things and airplane wheels. Silicone rubbers work in many temperatures and are used for wire covers.
Santoprene is known for being bendy and tough. Factories use santoprene in car seals, hoses, home machines, and things for outside. Santoprene can be recycled and shaped easily, so it is a top pick for cars and home goods. Vulcanization makes santoprene stronger and last longer, so it works in hard places. Vulcanization also lets santoprene be used again, which helps the planet.
Tip: Always pick the right rubber for the job. Use santoprene for bendy seals, NBR for oil, and EPDM for outside use.
Comparison of Types
Summary Table
The table below helps compare different types of synthetic rubber. It shows how they perform, how long they last, and how much they cost. This makes it easier to see which type is best for each job.
| Type | Key Strengths | Durability | Cost Level | Common Uses |
| SBR | Good abrasion resistance, easy to make | Moderate | Low | Tires, shoe soles, belts |
| NBR | Resists oil and fuel, strong | Moderate (poor UV/ozone) | Low | Seals, hoses, fuel systems |
| EPDM | Handles weather, UV, and chemicals | High | Moderate | Car seals, roofing, outdoor parts |
| Neoprene (CR) | Resists oil, chemicals, and weather | Moderate | Moderate | Gaskets, wetsuits, belts |
| Butyl (IIR) | Keeps air in, blocks gas | High (poor oil/ozone) | Moderate | Tire tubes, seals, stoppers |
| Silicone | Handles heat, cold, and UV | High | High | Medical, electronics, baking |
| Fluorocarbon (FKM) | Resists harsh chemicals and heat | High | High | Aerospace, chemical plants |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Strong against wear and tear | Moderate (poor UV/ozone) | Moderate-High | Wheels, bushings, machinery |
Note: Synthetic rubber can be made for special jobs. Some types last longer in hard places. Others cost less or work better with oil.
Choosing the Right Type
Picking the right synthetic rubber depends on what you need. Here are some steps to help you choose:
Check the environment: Will it face heat, cold, sun, or chemicals? Use EPDM or silicone for outside. Pick NBR for oil or fuel.
Think about strength: Does it need to stretch or stay firm? Polyurethane is tough and does not wear out fast. Silicone stays bendy in hot and cold.
Look at cost: SBR is cheap and works for many things. Silicone and fluorocarbon cost more but last longer in tough places.
Match the use: SBR and butyl rubber are used for tires. Silicone is safe for medical and food jobs. NBR or fluorocarbon are good for engine seals.
Check rules and safety: Some jobs need rubber that meets safety rules. Always check if the type is approved.
There are many kinds of synthetic rubber to pick from. Each one has special features for different jobs. By thinking about the job, where it will be used, and the budget, you can choose the best rubber for your project.
Synthetic rubber types are not all the same. Some are stronger or more bendy than others. Some can handle heat, oil, or bad weather better. Picking the right type makes things last longer and work well. This table helps makers choose the best rubber for each job:
| Type | Key Properties | Best Uses |
| NBR | Oil and fuel resistance | Engine seals, hoses |
| EPDM | Weather and heat resistance | Roofing, car seals |
| Neoprene | Chemical and fire resistance | Wetsuits, gaskets |
| Silicone | High heat and flexibility | Medical, kitchenware |
| Viton | Extreme chemical and temperature resistance | Aerospace, O-rings |
Santoprene is known for being bendy and tough in cars and home items.
FAQ
What is the main difference between natural and synthetic rubber?
Natural rubber comes from trees. Synthetic rubber is made in factories from oil chemicals. Synthetic rubber can be changed for special jobs. Both types can stretch and go back to their shape. Synthetic rubber usually lasts longer in hard places.
Which synthetic rubber works best for car tires?
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and butadiene rubber (BR) are best for car tires. They do not wear out fast and can take heat. Tire makers mix SBR with natural rubber to make tires stronger and last longer.
Can synthetic rubber be recycled?
Yes, many kinds of synthetic rubber can be recycled. Santoprene is easy to recycle. Recycling helps cut down on waste and saves materials. Some recycled rubber is used for new car parts, floors, or playgrounds.
Why do some rubbers resist oil and chemicals better than others?
Nitrile (NBR) and fluorocarbon (Viton) have special chemical makeups. These block oil and chemicals from hurting the rubber. That is why they are good for seals, hoses, and gaskets in engines and factories.
Is silicone rubber safe for food and medical use?
Yes, silicone rubber is safe for food and medical things. It does not react with most chemicals and can take high heat. Hospitals use silicone for tubes and implants. Food makers use it for baking mats and kitchen tools.



